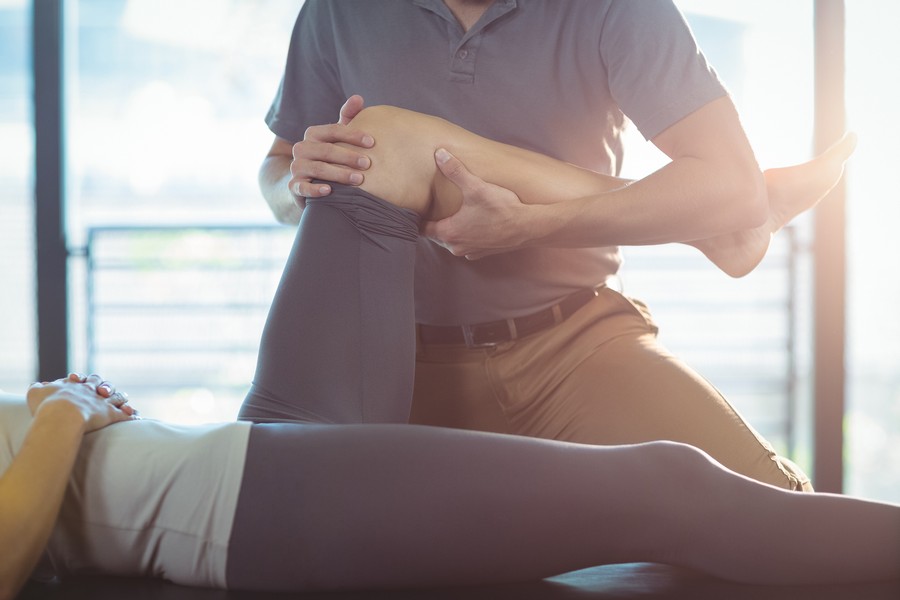
Leg Length Discrepancy (LLD) is a common orthopedic condition in both kids and adults in which one leg is slightly longer than the other. LLD affects up to 90% of the general population and is usually mild, causing no noticeable symptoms. However, a significant LLD can cause issues such as pain, gait abnormality, spinal deformity, and joint degeneration. In this article, we’ll discuss the types and symptoms of LLD, as well as diagnosis and treatment options for LLD.
Leg Length Discrepancy (LLD) is a common orthopedic condition in both kids and adults in which one leg is slightly longer than the other. LLD affects up to 90% of the general population and is usually mild, causing no noticeable symptoms. However, a significant LLD can cause issues such as pain, gait abnormality, spinal deformity, and joint degeneration. In this article, we’ll discuss the types and symptoms of LLD, as well as diagnosis and treatment options for LLD.
Types of Leg Length Discrepancy
LLD is classified into two types depending on the underlying cause:
- Structural (anatomical) – this is caused by a physical difference in bone lengths. An LLD can occur from birth or be acquired through a tumor, radiation, infection, or injury.
- Functional – this is when the legs appear to be different lengths but are not. Functional LLD happens due to an imbalance or asymmetry in the lower limb mechanics, including poor posture, muscle weakness, or joint contracture.
The severity of LLD is classified based on the size of the leg length discrepancy:
- Mild – 0-30 mm
- Moderate – 30-60 mm
- Severe – greater than 60 mm
Symptoms of Leg Length Discrepancy
Symptoms of LLD vary depending on the severity of the condition. In most cases, LLD is less than 10 mm and causes no noticeable symptoms; however, more significant discrepancies can lead to signs and symptoms, including:
- Walking with a limp or toe-walking
- Back, hip, knee, or ankle pain
- Postural abnormalities, such as a curved spine or tilted shoulder
Diagnosis of Leg Length Discrepancy
LLD can be diagnosed by clinical examination by a doctor or physiotherapist, using tools such as a tape measure, goniometer, or level to compare the lengths and angles of the legs. Additionally, imaging studies such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to measure the leg lengths more accurately and to determine any bone or tissue abnormalities that may be contributing to the LLD.
Treatment of Leg Length Discrepancy
Treatment of LLD depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause of the condition. Conservative options include observation, physiotherapy, and shoe modifications. Surgical options aim to slow down or stop the growth of the longer limb, lengthen the shorter limb, or shorten the longer limb using various techniques.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Leg Length Discrepancy
If you have noticed symptoms of LLD, you may benefit from physiotherapy, which involves an individualized treatment plan that is tailored specifically to the type and severity of your LLD.
Your physiotherapist can help to assess and treat the underlying cause of your LLD, such as muscle weakness and postural issues. After your assessment, your physiotherapist will create an individualized program that is specific to your needs and provide you with education, stretching and strengthening exercises, and shoe modifications to help balance your leg lengths and manage your symptoms. If your LLD is significant, and is beyond what can be corrected via physiotherapy, your physiotherapist may refer you to a specialist to have custom footwear made or for an orthopaedic surgical consult.
References
- Applebaum A, Nessim A, Cho W. Overview and spinal implications of leg length discrepancy: Narrative review. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery. 2021;13(2):127.
- Eliks M, Ostiak-Tomaszewska W, Lisiński P, Koczewski P. Does structural leg-length discrepancy affect postural control? Preliminary study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017;18(1):346.
- Lower limb length discrepancy - OrthoInfo - AAOS. OrthoInfo. September 2021.
- Vogt B, Gosheger G, Wirth T, Horn J, Rödl R. Leg length discrepancy— treatment indications and strategies. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 2020;117(24):405-411.