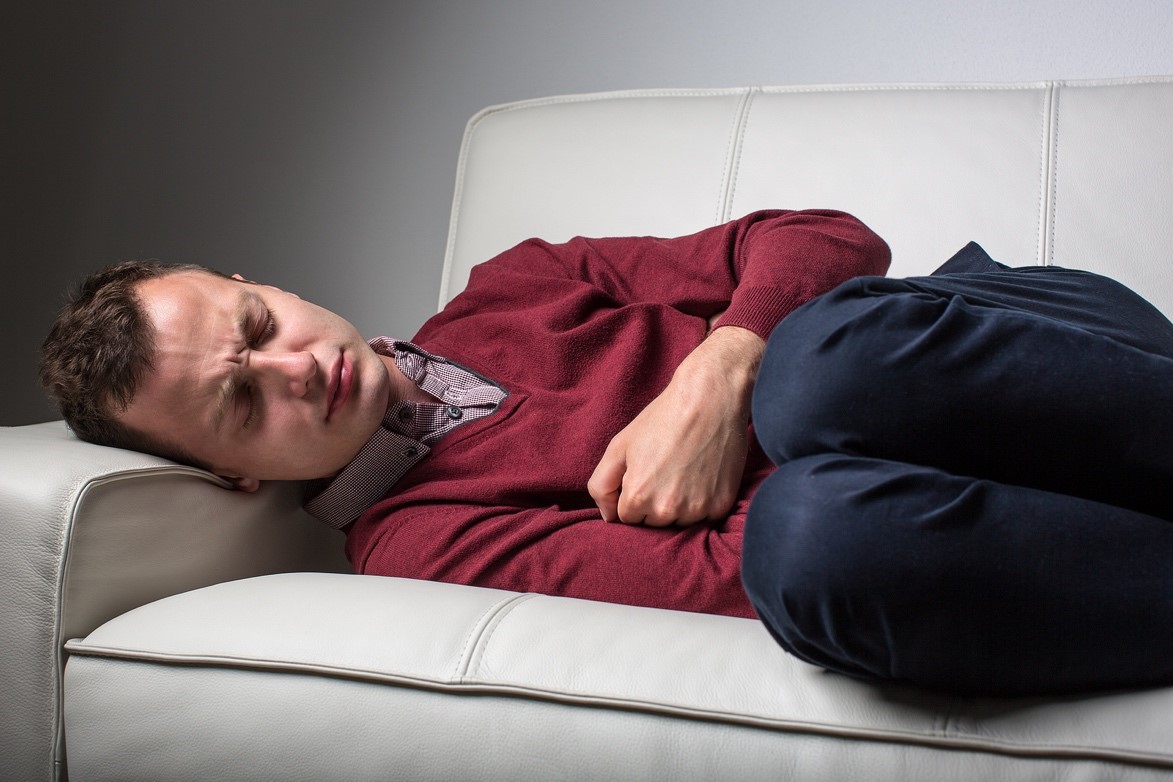
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are both types of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases that have similar symptoms and lead to digestive disorders and inflammation throughout the digestive system. While they do have similarities, they are two distinct conditions that require proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease can affect any part of your gastrointestinal (GI) tract from your mouth to your anus, although it most commonly affects the small or large intestine. It often involves patches of inflammation interspersed with healthy tissue. The inflammation can penetrate multiple layers of your bowel wall, which can lead to complications, including strictures, phlegmons, fistulas, and abscesses.
Crohn’s disease is chronic and often progressive. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease vary and range from mild to severe, depending on the area affected and how badly it is damaged. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease commonly include abdominal pain, non-bloody diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Other symptoms may include eye pain or redness, fever, anemia, mouth sores, joint soreness or pain, tiredness, and skin changes that include tender, red bumps under your skin.
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is limited to the large intestine (colon) and rectum. Ulcerative colitis leads to swelling and ulcers in the innermost layer of your colon. The inflammation associated with ulcerative colitis is continuous without gaps of healthy tissue.
Symptoms often come in waves and range in severity from mild to severe, depending on the extent of damage to your colon. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, an urgent need to empty your bowels, and diarrhea with mucus or blood. Complications of ulcerative colitis can be severe and include dehydration, rectal bleeding, a perforated colon, and toxic megacolon.
Treatment of Crohn’s Disease and Colitis
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are both treated with similar types of medications, including anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics, but the specific drugs vary between the two conditions. While ulcerative colitis is usually managed with medications that target the colon and rectum, Crohn’s disease often needs more aggressive surgical treatment than ulcerative colitis because it can affect any part of your gastrointestinal tract and can penetrate through multiple layers, leading to more extensive damage and an increased risk of complications.
The Role of Your Physiotherapist in Managing Crohn’s Disease and Colitis
If you’ve recently been diagnosed with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, be sure to speak to your physiotherapist. They can play a valuable role in improving your quality of life with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, addressing both your physical and emotional needs.
Your physiotherapist can use techniques such as manual therapy, soft tissue therapy, and the application of various modalities, including heat therapy and interferential therapy, to help alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with these inflammatory bowel conditions. Further, your physiotherapist can develop an individualized exercise program to improve your physical fitness, decrease your stress levels, and improve your stamina. Your physiotherapist can also educate you on your condition, outline the benefits of staying active, and discuss ways to manage your symptoms effectively. They can also provide you with emotional support and motivation, helping you to stay on track with your physical activity, even when you’re suffering a Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis flare-up.
References
-
Seyedian SS, Nokhostin F, Malamir MD. A review of the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment methods of inflammatory bowel disease. J Med Life. 2019;12(2):113-122. doi:10.25122/jml-2018-0075
-
Ranasinghe IR, Tian C, Hsu R. Crohn Disease. [Updated 2024 Feb 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436021/
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Crohn’s Disease Basics. Published on June 21, 2024. Accessed October 6, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/inflammatory-bowel-disease/about/crohns-disease-basics.html.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Crohn’s Disease Basics. Published on June 21, 2024. Accessed October 6, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/inflammatory-bowel-disease/about/crohns-disease-basics.html.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ulcerative Colitis Basics. Published on June 21, 2024. Accessed October 6, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/inflammatory-bowel-disease/about/ulcerative-colitis-uc-basics.html.